Servlet JSP 复习
What is web container ?
Web container is the component in J2EE which is responsible for handle request from client. Web Server application like tomcat is used to support basic service for web container, e.g., receive request and forward reply to client.
What is Servlet ?
An important base class in J2EE which is the service unit for request of client.What is JSP technology ?
JavaServer Pages enable you to write standard HTML pages containing tags that run powerful programs based on Java technology.What technology is used to implement the session management in J2EE ?
Cookie, URL-rewriting, Hidden form field, Servlet Session API.
What is business tier? How to use it? (draw a chart to explain)
Business code or tier, which is logic that solves or meets the needs of a particular
business domain such as banking, retail, or finance.
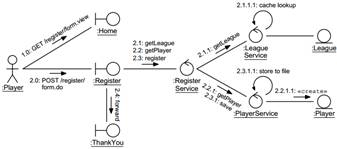
- How does J2EE web container work? (draw a chart.)
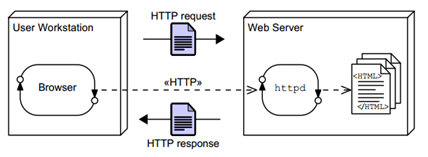
What is JNDI and JDBC?
JNDI is Java Naming and Directory Interface. A naming context is a set of name-to-object bindings. A name that is bound within a context is the JNDI name of the object, with which, application can find resource or object easily. In the JNDI, databases are accessed via DataSource objects.
What scopes can be used to share objects between Servlets (lists at least 3.)
request, response, ServletContext, Session
What is Authentication and Authorization in J2EE?
Authorization provides controlled access to protected resources. Authorization is based on identification and authentication. Authentication is a process that verifies the identity of a user, device, or other entity in a computer system, usually as a prerequisite to allowing access to resources in a system.
What is ServletContext?
Defines a set of methods that a servlet uses to communicate with its servlet container, for example, to get the MIME type of a file, dispatch requests, or write to a log file.
What is FilterChain in J2EE?
A FilterChain is an object provided by the servlet container to the developer giving a view into the invocation chain of a filtered request for a resource. Filters use the FilterChain to invoke the next filter in the chain, or if the calling filter is the last filter in the chain, to invoke the resource at the end of the chain.
What is servlet life cycle? (Draw a chart to explain)
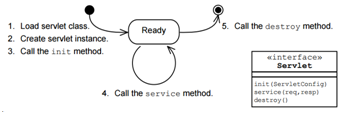
What is DAO design pattern?
The DAO design pattern (2 of them): 1) Separates object persistence and data access logic from the business logic or persistence mechanism API. 2) Enables you to change the data access code at any point in time without modifying the application code. 3) Can be implemented by using various interfaces, frameworks, and commercial products that can separate the data access from the application logic. 4) Is implemented in the Java technology, Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI).
What is Data Integrity and Auditing in J2EE security?
Data Integrity: Ensures that data is not modified while being transferred between the server and the client.
Auditing: Secures Web applications by maintaining a record of the rights assigned to different types of Web users.
1 | getServletConfig().getInitParameter("fileName")); |